Have you or a loved one experienced COVID-19 coronavirus infection, and you need additional information about rehabilitation after the disease? This article is for you!
Rehabilitation after a COVID-19 coronavirus infection is an important stage in body recovery, which will help you return to a full life and avoid potential complications. We invite you to delve into the topic and learn about a variety of rehabilitation approaches, including treatment and support for various body systems.
In this article, we will look in detail at various aspects of rehabilitation after COVID-19, including the treatment process for myocarditis, care for the vocal cords, throat and larynx, restoration of smell, skin and hair support, as well as mental condition. We will also tell you about proven medications and locations where you can undergo a rehabilitation course.
Don’t delay until tomorrow – start reading the article right now to get all the necessary information about rehabilitation after a COVID-19 coronavirus infection and start your path to health recovery!
General Information
COVID-19 coronavirus infection has a serious impact on people’s health, especially the respiratory system. An important aspect of recovery is rehabilitation after the coronavirus, which helps you restore health and return to active life.
Etiology and Pathogenesis
COVID-19 is caused by a new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. The virus affects the body, causing inflammation and dysfunction of various organs and systems, including the lungs, heart, circulatory system, and nervous system.
Clinical picture: Symptoms, course
The symptoms of the coronavirus infection vary from mild to severe. Typical symptoms are fever, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, loss of smell and taste, headaches, and myalgia. Some patients may develop complications requiring hospitalization and intensive therapy.

How does rehabilitation after COVID-19 proceed?
Vocal cords, throat, and larynx
After the coronavirus infection, hoarseness, throat irritation, and painful swallowing may persist. Phytotherapy, gargling with chamomile and calendula infusions, as well as an appropriate diet and rest regimen contribute to the restoration of the vocal cords, throat, and larynx.
Smell
Loss of smell is a common phenomenon after COVID-19. The recovery of smell can take from several weeks to months. Practicing aromatherapy and familiarizing yourself with various aromas contributes to quick recovery.
Skin and Hair
COVID-19 can cause skin manifestations such as rash, redness, and itching. Skin recovery includes using mild moisturizers, applying sun protection, and adequate nutrition. Periodic stresses associated with the coronavirus infection can cause hair loss. It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, adequate intake of vitamins and minerals to restore hair health.
Mental Health
The consequences of COVID-19 can affect mental health, causing anxiety, depression, and stress. Psychological support, meditation, regular physical activity, and proper nutrition will help cope with mental stress.
Muscular System
Muscle weakness and fatigue are common consequences of the coronavirus infection. Physical rehabilitation, including exercises to develop muscle strength and endurance, will help restore the functioning of the muscular system.
Medications for Rehabilitation After COVID-19 Treatment
Various medications may be used during rehabilitation after COVID-19, aimed at improving the condition of the body and restoring functions affected by the infection. However, specific drugs and their dosage should be selected individually, taking into account a patient’s condition and doctor’s recommendations. Below are some examples of drugs that have undergone clinical trials and proven their effectiveness in rehabilitation of patients after COVID-19.

Antioxidants
Drugs containing antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, selenium, zinc, coenzyme Q10, may be useful for relieving oxidative stress and restoring cellular functions. They promote tissue healing and facilitate recovery after infection.
Mucolytics
Drugs that facilitate the expectoration of mucus, such as acetylcysteine (ACC), ambroxol, carbocisteine, may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms associated with respiratory diseases.
Bronchodilators
Medications that dilate the bronchi and facilitate breathing, such as salbutamol, formoterol or theophylline, may be used to relieve bronchospasm and improve respiratory function.
Corticosteroids
In some cases, when there is pronounced inflammation and swelling, corticosteroids, such as prednisolone or dexamethasone, may be prescribed. They help reduce inflammation and swelling, improving a patient’s overall condition.
Immunomodulators
Drugs that stimulate the immune system, such as interferons, immunoglobulins, extracts of echinacea or cordyceps, may be used to strengthen the immunity and support the body during rehabilitation. They can help accelerate recovery and prevent possible complications after COVID-19.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
After treatment for the coronavirus infection and the use of antibiotics, the gut microbiota may be impaired. Probiotics (e.g., lactobacilli and bifidobacteria) and prebiotics (e.g., inulin and oligosaccharides) can help restore the normal balance of microorganisms in the gut and support the immune system.
Vitamin D
The level of vitamin D in the body plays a crucial role in rehabilitation after COVID-19. Vitamin D improves the functioning of the immune system and promotes quick recovery. It is recommended to consult a doctor about the need for additional intake and the determination of the optimal dose.
Cardioprotectors
In cases of cardiovascular disorders after COVID-19, drugs that prevent the further development of cardiovascular diseases may be prescribed. These could be anticoagulants, statins, antihypertensive drugs or antiarrhythmics.
Nootropics and Adaptogens
For the recovery of nervous system functions and reducing fatigue, nootropics (e.g., piracetam, glycine) and adaptogens (e.g., ginseng, Rhodiola rosea, Baikal skullcap) may be used. They can help improve cognitive functions, reduce stress levels, and improve the body’s adaptation to stresses.
It’s important to understand that drug rehabilitation after COVID-19 should be conducted under the supervision of a doctor, who can modify the treatment plan depending on the dynamics of a patient’s condition and the occurrence of possible side effects. Administration of drugs without the control of a specialist can lead to unpredictable consequences and complications.
Complication after the Coronavirus Infection: Myocarditis
Myocarditis is an inflammatory disease of the heart muscle (myocardium), which can occur as a complication after the coronavirus infection. COVID-19 can affect the heart muscle and cause myocarditis directly or indirectly, through the body’s immune response to the infection.
Symptoms of Myocarditis
Symptoms of myocarditis can range from mild to severe and include:
- Chest pain or discomfort;
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion;
- Involuntary rapid heart rate (tachycardia);
- Swelling of the legs, ankles and feet;
- Fatigue and weakness;
- Dizziness, loss of consciousness or fainting.
Diagnosis of Myocarditis
To diagnose myocarditis, a doctor may refer to the following tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): to detect heart rhythm abnormalities and other disorders;
- Echocardiogram: to evaluate the structure and function of the heart;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the heart: to detect myocardial inflammation;
- Blood test: to determine the level of cardiotropic viruses and other markers of inflammation;
- Heart catheterization and myocardial biopsy: in some cases, to determine the cause of inflammation.
Treatment of Myocarditis
The treatment of myocarditis depends on its severity and cause. The doctor may recommend the following therapeutic measures:
- Rest and reduced physical activity during recovery;
- Antibiotics if myocarditis is caused by a bacterial infection;
- Administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve inflammation and pain;
- Administration of corticosteroids in cases of severe inflammation or autoimmune myocarditis;
- Administration of diuretics to reduce swelling and mitigate the load on the heart;
- Treatment of heart failure with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors), beta-blockers and other drugs if necessary;
- Administration of antiarrhythmic drugs to correct heart rhythm disorders;
- In some cases, immunoglobulins or other immunomodulators may be taken to support the immune system.
Recommendations and Prevention of Myocarditis after COVID-19 Coronavirus Infection
To prevent the development of myocarditis and reduce the risk of complications after the coronavirus infection, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Consult a doctor promptly when symptoms of the coronavirus infection appear and strictly follow the prescribed treatment.
- After recovery, consult a cardiologist and undergo a comprehensive examination to identify possible heart abnormalities.
- Adhere to a rest and reduced physical activity regimen during recovery and as recommended by the doctor.
- Monitor your health condition and undergo regular medical check-ups, even if there are no symptoms of myocarditis.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, follow a balanced diet and engage in physical activity as much as you can after completing rehabilitation.
- Avoid stress and nervous tension, as they can negatively affect the cardiovascular system.
Timely diagnosis and treatment of myocarditis, as well as strict adherence to doctors’ recommendations, will minimize the risk of complications and improve the prognosis for recovery.
Video: “Rehabilitation after COVID-19 Coronavirus Infection”
Exercises for post-COVID rehabilitation. The first (1) direction: rehabilitation of the respiratory system
For additional information about the recovery process after COVID-19 Coronavirus Infection, you can watch a video demonstrating exercises and rehabilitation recommendations.
Where can I undergo rehabilitation after COVID-19?
The selection of a facility for rehabilitation depends on the individual needs of any patient and the availability of specialized centers. Among the possible options, there are:
- Rehabilitation in clinics;
- Health resorts;
- Specialized medical centers;
- At home.
It’s important to select a medical facility with the experienced staff and a comprehensive approach to the recovery process.
What kind of rehabilitation should I undergo after COVID-19
Let’s take a closer look at 3 types of rehabilitation:
- Home-based recovery;
- Rehabilitation in a clinic after the acute process has subsided;
- Sanatorium-resort treatment.
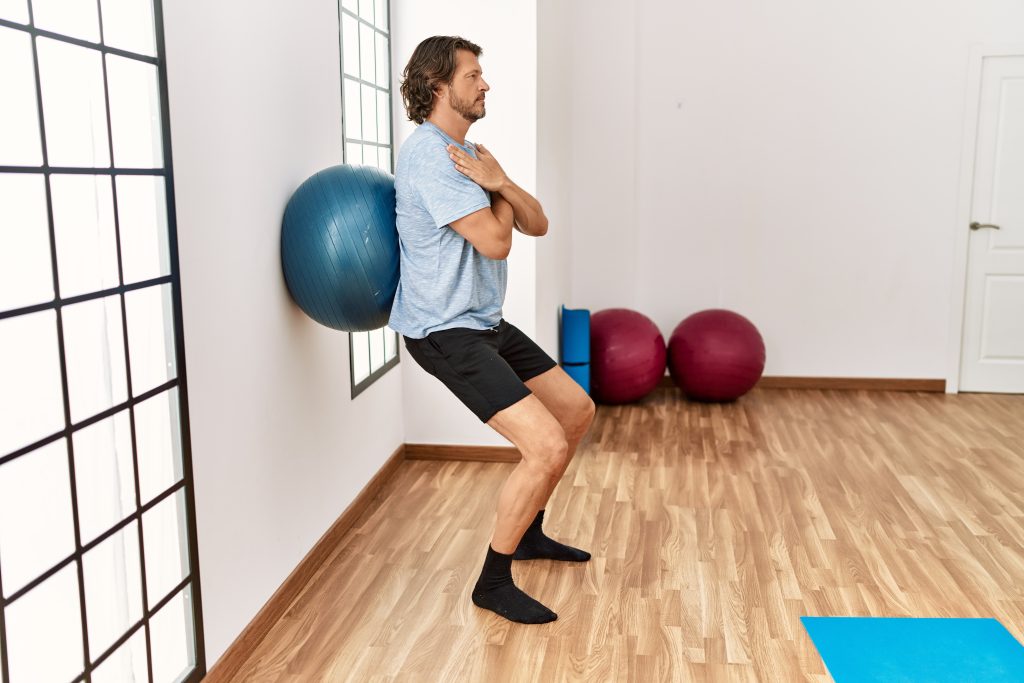

Home-based Rehabilitation
Home-based rehabilitation is suitable for those who have had a mild form of COVID-19 and do not have any serious complications. It includes respiratory exercises, exercises to develop muscle strength, as well as adherence to proper nutrition and daily routine. Regular consultations with a doctor are also an integral part of home rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation in a clinic after the acute process has subsided
Patients with complications or severe COVID-19 may require more intensive rehabilitation in specialized clinics or medical centers. Here patients are provided with individual recovery programs, which may include physiotherapy, massage, special workouts, as well as medication and psychological support.
Health Resort Treatment
Health resort rehabilitation is a comprehensive recovery program that combines medical and wellness procedures. It is suitable for patients with residual symptoms and disorders of various organs and systems. Health resort treatment may include a course of therapy with mineral waters, mud therapy, hydrotherapy, as well as various types of massage and physiotherapy. In addition, health resorts provide a calm and relaxing atmosphere, which contributes to the recovery of a patient’s psycho-emotional condition.
The selection of a particular type of rehabilitation depends on a patient’s condition, the presence of complications and the recommendations of the treating doctor. It is important to take into account the individual characteristics of the body and the needs of each patient in order to ensure the most effective and safe recovery after the coronavirus.
The Importance of a Comprehensive Approach to Rehabilitation after COVID-19
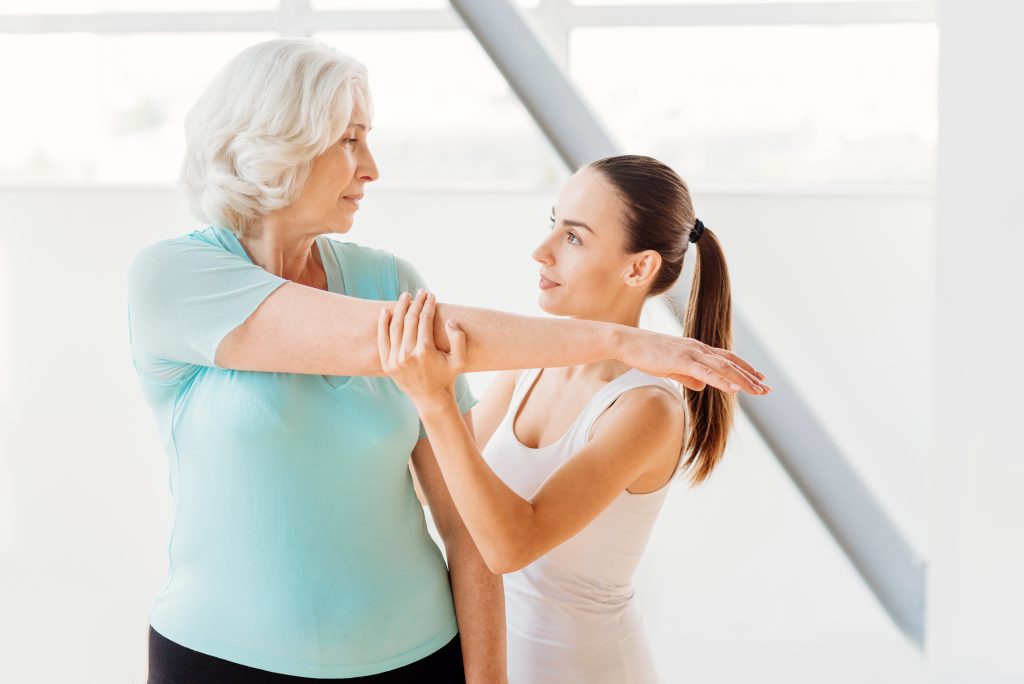

Monitoring Health Status
A key aspect of successful rehabilitation after COVID-19 is regular monitoring of a patient’s health status. Doctors should monitor the dynamics of the body’s function recovery and, if necessary, modify the rehabilitation program. This may include changing the loads during physical exercises, modifying/correcting the diet, and administration of specific drugs special medical drugs.
Psychological Support
Many patients face psychological difficulties after the coronavirus infection, such as anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder. It’s important to provide psychological support and help in while coping with these conditions, as they can slow down the recovery process. Doctors and psychotherapists can offer various methods and techniques for managing stress, as well as the opportunity for group or individual therapy.
Social Adaptation
After the coronavirus infection, many patients have difficulty adapting to everyday life and work. It’s important to help them regain skills and confidence that they successfully return to active life. This may include consultations with employment professionals, working with social services, and providing information about possible rights and benefits for people who have had COVID-19.
Conclusion
The importance of rehabilitation after the coronavirus infection COVID-19 cannot be underestimated. Successful recovery from the disease depends on a comprehensive approach, including respiratory, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, and muscle rehabilitation, as well as managing the syndrome of general fatigue and restoring balance.
Individual respiratory rehabilitation, such as respiratory gymnastics, will help improve lung function and eliminate residual effects of inflammation. Cardiovascular rehabilitation, including moderate aerobic activity, contributes to the strengthening of the heart muscle and the improvement of circulation.
Rehabilitation of the musculoskeletal system and muscle apparatus, for example, exercises for strengthening muscles and joints, reduces the risk of chronic fatigue and dysfunction. Managing the syndrome of general fatigue involves restoring energy, strength, and endurance with rational nutrition, sufficient sleep, and rest.
Restoring balance and eliminating dizziness can be achieved with specialized exercises aimed at improving vestibular function and coordination of movements.
In general, a comprehensive and individually tailored rehabilitation program that takes into account all aspects of recovery is a key to successful recovery after COVID-19. Be sure to follow the recommendations of doctors and do not forget about individual exercises to return to a full life after the disease.
Check out the demo version of our exercises for post-COVID rehabilitation on YouTube.
You can find more information about the Rehabilitation after COVID-19 by in our Library of Articles.
Our website presents sets of exercises for rehabilitation after COVID-19 in the following four areas:



