Rehabilitation after a Hand Fracture: How Long to Work on a Hand After a Fracture and What Measures to Take?
No one can avoid life’s falls and blows, which often lead to bone fractures. Hand trauma is an injury to the bone of the upper limb, including the humerus, forearm, elbow joint, wrist, or fingers. To restore the functionality of the limb after a fracture, rehabilitation is necessary, which includes special exercises and massage. This article will discuss various aspects of rehabilitation and how long it takes to work on a hand after a fracture, as well as possible rehabilitation measures needed after upper limb injuries.
There are various types of injuries that can be classified depending on the part of the body affected, severity, and distinctive features.
Rehabilitation After a Wrist Fracture
A wrist fracture is one of the most common types of injuries. It is important to know that rehabilitation after a wrist fracture should start as soon as possible. This will help shorten the recovery period and return to normal life faster. First of all, you should see a doctor who will prescribe the appropriate set of procedures and exercises for rehabilitation.
Types of Fractures
There are many types of fractures, which can be divided into open and closed, as well as by the degree of displacement of bone fragments. Depending on the type of fracture, the doctor will determine an individual treatment and rehabilitation plan.
Injuries can be divided into two categories: complicated and uncomplicated. Complicated injuries are those that are accompanied by bleeding and blood infection, while uncomplicated injuries do not have these additional complications.
Exercise Complexes for Rehabilitation

To lead a full life, it is very important to regulate the functions of the hands. This includes appropriate methods of rehabilitation after any hand injuries in order to restore the hand’s functionality.
Patients often find that their hand feels alien after the cast is removed, as the limb has been immobile for a long time, leading to muscle weakening and a deterioration of blood flow to the tissues. While the bone parts can be restored, the functions of the hand may not be fully recovered. Full recovery through rehabilitation usually can take from a few weeks to several months.
Rehabilitation Complex After Removing the Cast
After removing the cast, the hand may be weak and inflexible. It’s important to start a set of exercises that will include different types of movements: bending and extending, rotating, spreading, and bringing fingers together.
During rehabilitation after a wrist fracture, it is important to select suitable exercises that gradually increase in complexity and include both active and passive loads. Individual physical characteristics and the nature of an injury should be taken into account.
After the cast is removed, certain exercises are recommended, including:
- Finger squeezing;
- Keeping the palm part in a “scissors” position;
- Joining the thumb and forefinger into a ring while relaxing other parts of the upper limb;
- Holding the palms in a “goat” position;
- Positioning the thumb, forefinger, middle, and ring fingers into a semi-circle;
- Folding the injured hand into a “victory” sign and stretching the upper back;
- Clasping the tops of both palms in a “goat” position and pulling in opposite directions;
- Interlocking the inner parts of the wrists and pushing them apart;
- Squeezing the injured hand into a fist, sticking out the index finger and pulling it up with the other hand;
- Pressing each finger in turn to a solid surface;
- Making different shapes out of matchsticks;
- Tying shoelaces and fastening hooks.
Exercises can also be performed in water, for example, lifting small objects from the bottom of a bathtub or bucket, such as nuts or scattered change.
Home Rehabilitation Exercises

At home, various exercises can be performed, such as squeezing a soft ball or rubber expander, lifting and dropping small objects from the floor, massaging fingers and wrist, as well as doing baths with warm water and salt.
Rehabilitation exercises at home will help you accelerate the process of restoring hand functions after a fracture. It’s important to perform them correctly and regularly, following the instructions of your doctor or physiotherapist.
Using Play-Doh
Working with Play-Doh can be a useful exercise for restoring mobility and strength to the wrist after a fracture. Play-Doh provides resistance that trains the muscles and joints.
- Take some Play-Doh and soften it in your hands.
- Form a ball from the Play-Doh and put it on the table.
- Using the fingers of the injured hand, press on the ball, performing different movements: squeezing, unsqueezing, rolling, etc.
- Perform the exercise for 5-10 minutes several times a day.
Stimulating Blood Circulation
Improving circulation in the area of the fracture promotes a rapid healing of bones and tissue regeneration.
- Raise your hand above the level of your heart to reduce swelling.
- Make slow circular movements with your wrist, first in one direction, then in the other.
- Perform this exercise for 5 minutes, several times a day.
Throwing and Catching a Ball
Throwing and catching a ball helps develop coordination, strength, and mobility of the injured hand.
- Take a small soft ball, a tennis ball will do, and sit or stand in a comfortable position.
- Throw the ball with your injured hand and catch it with your healthy one.
- Gradually increase the distance between your hands and the complexity of the exercise.
- Perform this exercise for 10-15 minutes, several times a day.
Exercise to Alleviate Swelling
Swelling after a fracture can cause discomfort and slow down the recovery process. Performing exercises to relieve swelling can improve the overall condition of your hand and accelerate rehabilitation.
- Sit or lie down, placing the injured hand on a pillow so it’s above the level of your heart. This helps reduce swelling by decreasing venous pressure.
- Slowly squeeze and release your hand several times, trying not to cause pain.
- Repeat this exercise several times a day, especially after performing other rehabilitation exercises.
Following these exercises and performing them correctly, you will be able to restore the functions of your hand after a fracture at home. However, it’s important to remember that recovery after a fracture is an individual process, and you may need more or less time for rehabilitation depending on the complexity of the injury and your health condition. Always follow the recommendations of your doctor and don’t hesitate to consult with him if you have any questions or problems.
Video: “Rehabilitation after a Hand Fracture”
Upper limb. Set No.1 improvement of mobility and range of joint movement
For additional information about the recovery process after a hand fracture, you can watch a video demonstrating exercises and rehabilitation recommendations.
Recovery After a Wrist and Finger Fracture
Recovery after a wrist and finger fracture requires a special approach and a set of exercises. It’s important to start rehabilitation as soon as possible to prevent complications and restore hand functions.

Identifying the Fracture
Wrist and finger fractures can be identified by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the area of the injury, which intensifies with movement or load on the hand.
- Swelling and bruises in the area of the fracture.
- Bone deformation or incorrect position of the fingers.
- Limited movement or complete immobility of the hand.
The final diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after conducting an X-ray examination.
Applying a Cast
A cast is typically applied in cases of:
- Open and closed fractures with bone integrity impairment.
- Fractures with displaced bone fragments.
- Stable fractures to provide immobilization and accelerate healing.
A cast should be by a professional to ensure proper fixation of the bones and prevent possible complications.
Rehabilitation Exercises
After removing the cast, it’s essential to start a set of exercises to regain mobility, strength, and coordination of the hand. Here are a few fundamental exercises:
- Squeeze and release the hand: Slowly and in the controlled way, squeeze and release the hand, repeating the exercise 10-15 times, several times a day.
- Circular hand movements: Perform slow circular hand movements in both directions, repeating the exercise 10-15 times, several times a day.
- Stretching the fingers: Ask someone to help you gently stretch your fingers, pausing at the maximum stretch point for a few seconds, then slowly returning to the initial position. Repeat the exercise 5-10 times for each finger several times a day.
- Bending and extending the fingers: Slowly and in the controlled way, bend and extend your fingers, performing the exercise 10-15 times, several times a day.
- Resistance of the fingers: Use a rubber or textile ring to create resistance when bending and extending the fingers. Repeat the exercise 10-15 times, several times a day.
Su Jok Massage Ring
A Su Jok massage ring is a tool for activating points on the fingers and hand, based on the principles of the Korean Su Jok therapy system. Recovery after a fracture may involve using a Su Jok massage ring to stimulate circulation, reduce swelling and pain, as well as improve overall hand mobility.
Use the Su Jok massage ring in the following way:
- Put the ring on a finger or the fractured area of the hand.
- Slowly move the ring up and down the finger or hand for 5-10 minutes without causing pain.
- Perform the procedure several times a day, especially after performing rehabilitation exercises.
- It’s important to remember that using the Su Jok massage ring should be comfortable and painless. If you experience pain or discomfort during the procedure, be sure to consult a doctor.
Contraindications
It’s important to know that in some cases, physical therapy and other rehabilitation procedures may be contraindicated. Understanding these limitations will help avoid possible complications and ensure a safe recovery after a fracture.
Contraindications to Physical Therapy
Physical therapy may be contraindicated in the following cases:
- Acute period of inflammatory diseases and infections.
- High body temperature.
- General weakness and exhaustion.
- Unstable condition of the fracture or incorrect bone healing.
- Presence of bone fragment displacement requiring surgery.
- Thrombosis or other circulatory disorders.
- Cardiovascular diseases where physical exertion may worsen the patient’s condition.
Contraindications to Rehabilitation Procedures
Some rehabilitation procedures also have their limitations and contraindications. Here are some of them:
- Massage: Contraindicated in acute inflammatory processes, infections, thrombosis, skin diseases, and injuries in the massage area.
- Physiotherapy: Contraindicated in acute inflammatory processes, infectious diseases, oncological diseases, severe cardiovascular disorders, and some other diseases.
- Manual therapy: Contraindicated in osteoporosis, congenital anomalies of the bone system, unstable fractures, infectious and inflammatory processes.
Before starting a rehabilitation course, it’s important to consult with a doctor who will conduct a full examination and determine which procedures and exercises are appropriate for your case. Remember that self-treatment can harm your health, so always follow the recommendations of professionals.
How long should I rehabilitate my hand after a fracture, and what rehabilitation measures should I take?
Recovery times after a hand fracture can vary depending on the severity of the injury, the patient’s age, overall health condition, and individual characteristics. On average, rehabilitation can take from 30 to 60 days. It’s important to patiently and consistently follow all of the doctor’s prescriptions/recommendations, as well as adhere to the treatment regimen and rules.
Types of Hand Fractures
The hand consists of multiple bones that can be susceptible to fractures. The upper limb is divided into several areas, each of which has its own features and types of fractures. Here is a detailed review of possible hand fractures:
Humerus Fractures
- Neck Fracture: A fracture of the neck of the humerus, often caused by a fall onto an outstretched arm or direct impact.
- Diaphyseal Fracture: A fracture of the diaphysis of the humerus, usually as a result of direct or indirect traumas, for example, when falling onto an outstretched arm.
Elbow Joint Fractures
- Olecranon Fracture: A fracture of the upper part of the ulna, usually caused by falling onto a bent arm.
- Radial Head and Neck Fractures: Fractures occurring in the elbow joint area, often associated with falling onto an outstretched arm.
Forearm Fractures
- Both Bone Forearm Fractures: Simultaneous fractures of the radius and ulna, often caused by a fall onto an outstretched arm or direct blow.
- Isolated Radius or Ulna Fractures: Fractures in which only one of the forearm bones is damaged.
Wrist Joint Fractures
- Distal Radius Fracture: A fracture in the wrist joint area, often caused by falling onto an outstretched arm with deviation of the wrist to the side.
- Ulnar Fracture in the Wrist Joint: A rare type of fracture, usually caused by a direct blow.
Hand Fractures
- Carpal Fractures: Fractures of the bones forming the base of the hand, usually caused by a punch or a fall onto a closed hand.
- Metacarpal Fractures: Fractures of the long bones located between the base of the hand and the phalanges of the fingers, can be caused by a blow, fall, or crushing.
- Phalangeal Fractures: Fractures of the finger bones, often caused by direct impact, crushing, or falling onto the fingers.
Finger Joint Fractures
- Interphalangeal Joint Fractures: Fractures affecting the finger joints, usually occur as a result of a direct blow or severe bending of the finger.
- Metacarpophalangeal Joint Fractures: Fractures occurring in the joint area connecting the metacarpal bones and the phalanges, usually caused by a blow or severe bending of the finger.
Causes of Fractures
Hand fractures can occur for various reasons, such as a bad fall, sports injuries, car accidents, or domestic accidents. In addition, some diseases, such as osteoporosis, can increase the risk of fractures.
Signs of Injury
Symptoms of a hand fracture can include pain, swelling, deformation at the site of injury, bruising, severe pain, limited movement, and sensory impairment. If a fracture is suspected, it is necessary to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
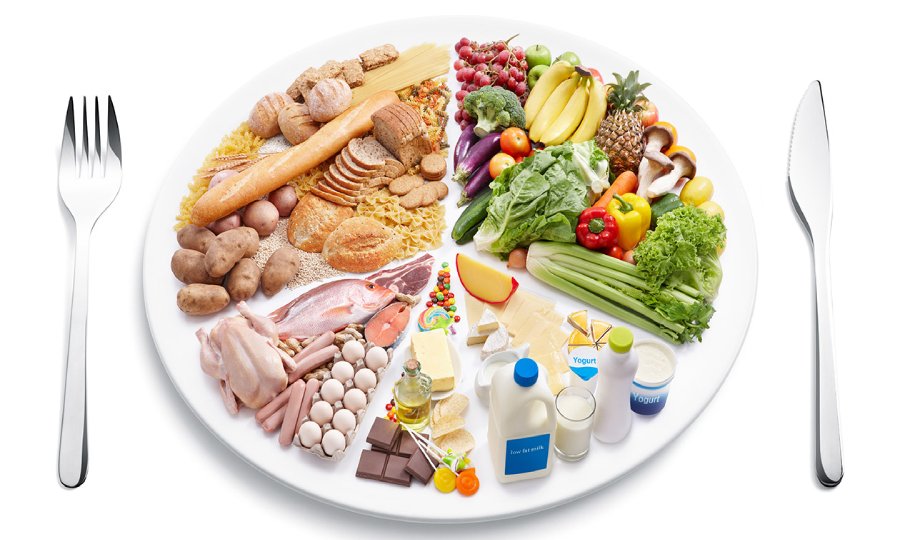

Diet During Rehabilitation
Adequate nutrition during rehabilitation is crucial as it helps the body restore damaged tissues and boost immunity. Your diet should include foods rich in calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, B vitamins, and vitamin D. Such foods include dairy products, fish, meat, nuts, green vegetables, and citrus fruits.
Adequate Nutrition During Rehabilitation
An important aspect of rehabilitation after a hand fracture is maintaining adequate nutrition. A balanced diet helps improve the overall condition of the body, accelerates healing and recovery processes.
Proteins
Your body needs proteins for tissue formation and recovery, especially during rehabilitation. Include meat, fish, dairy products, eggs, legumes, and nuts in your diet.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are necessary for maintaining health of the bones, muscles, and joints. Calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and vitamin D are particularly important. Consume dairy products, green vegetables, nuts, seeds, seafood, and fish.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants help reduce inflammation and accelerate the recovery process. Include fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains in your diet.
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, such as omega-3, help reduce inflammation and improve tissue healing. Consume seafood, fish, nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for your body. Include whole grain products, vegetables, fruits, and legumes in your diet.
Following an adequate diet during rehabilitation after a hand fracture will help up accelerate the healing and recovery process, as well as strengthen the immune system and overall health of the body.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is an important part of the rehabilitation process after a hand fracture. It involves various procedures aimed at improving circulation, reducing inflammation and pain, and stimulating the regeneration of tissues and joints. Let’s consider some of the most common physiotherapy procedures used in rehabilitation after a hand fracture.
Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy is the application of electric current to stimulate tissue regeneration, reduce pain and inflammation. It can be used to treat edema and improve nerve and muscle function. The most common types of electrotherapy are transcranial electrical stimulation (TES) and electromyostimulation (EMS).
Ultrasound Therapy
Ultrasound therapy uses high-frequency sound waves to stimulate circulation, reduce inflammation, and pain in the injury area. This method can also contribute to muscle relaxation and improve joint mobility.
Magnet therapy
Magneto therapy is based on the use of a magnetic field to improve circulation and tissue regeneration, as well as reduce pain and inflammation. This method can be used to stimulate healing processes and prevent the development of complications such as contractures and muscle atrophy.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is used to stimulate blood circulation and accelerate healing processes. It can help reduce pain, inflammation, and swelling, as well as stimulate the growth of new cells and strengthen the connective tissue.
Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy, or water treatment, uses the power of water to improve circulation, reduce pain and inflammation, as well as relax muscles and maintain joint mobility. During hydrotherapy, the patient can perform various exercises in water, which eases movement and reduces stress on the injured areas.
Heat and Cold Treatments
Heat and cold treatments can be used depending on the recovery stage after a hand fracture. In the early stage, when there is swelling and inflammation, cold compresses or ice packs are usually recommended. They help reduce pain, decrease inflammation, and control swelling. Once the swelling and inflammation have reduced, heat treatments such as heating pads, paraffin baths, or warm compresses can be applied to improve circulation, relieve muscle spasms, and improve joint mobility.
Exercises
Exercises are the primary method of restoring hand functions after a fracture. It’s important to perform exercises regularly and under the supervision of a specialist, as we have told before, to avoid possible complications.
Why Hand Rehabilitation is Important and Possible Consequences of Neglecting it
Rehabilitation and mobilization of the hand after a fracture are critical for restoring its functions and preventing complications. In this section, we will discuss why hand mobilization is important, and what consequences there could be if it’s neglected.
The Importance of Rehabilitation after a Fracture
- Restoring Motor Function: Rehabilitation helps restore normal joint mobility and muscle strength, enabling individuals to return to their daily activities and work.
- Improving Circulation: Regular exercises contribute to the improved blood circulation and tissue nutrition, which accelerates the healing process.
- Reducing Swelling: Rehabilitation helps reducing swelling and restoring the normal condition of surrounding tissues.
- Preventing Contractures: Early mobilization prevents the formation of contractures (muscle, ligament, and joint capsule shortening), which can limit joint mobility and cause chronic pain.
Consequences of Insufficient/Poor Rehabilitation
- Restricted Mobility: Failure to exercise the affected limb can lead to the reduced joint mobility, resulting in a prolonged functional impairment of the upper extremity.
- Muscle Atrophy: Without regular exercises, muscles may become atrophic, diminishing their strength and volume.
- Chronic Pain: Insufficient/poor rehabilitation can lead to chronic pain due to improper fracture healing or the development of contractures.
- Delayed Healing Process: Without rehabilitation, the fracture healing process may be delayed, increasing the risk of complications and prolonging the recovery period.
Rehabilitation Measures after a Hand Fracture
Rehabilitation measures following a hand fracture may include physical therapy, physiotherapy, massage, kinesio taping, and other methods that facilitate the restoration of upper extremity functions.
Additional Recommendations
In addition to the primary rehabilitation methods, the use of elastic bandages, orthopedic devices, and psychological support to help patients adapt to the limitations associated with a hand fracture may also be recommended.
Modern Rehabilitation Techniques
Modern rehabilitation techniques encompass various methods and approaches that aid in help restoring hand function after a fracture and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Kinesio Taping
Kinesio taping involves applying specialized elastic strips to the injured area to alleviate pain, reduce swelling, and improve blood circulation. This method can be used during the rehabilitation process after a hand fracture, following a doctor’s recommendation and under their supervision.
Therapeutic Massage
Therapeutic massage helps relax muscles, improve blood circulation, and reduce pain. During rehabilitation after a hand fracture, it is important to seek for a qualified massage therapist or learn self-massage techniques to perform massage correctly and safely.
Electromyostimulation
Electromyostimulation is a physiotherapy method in which an electrical impulse is applied to the injured muscles to stimulate their contraction. This method can be used during the rehabilitation process after a hand fracture to strengthen the muscles and improve their function.
Kaltenborn-Evjenth Manual Therapy
Kaltenborn-Evjenth manual therapy is a combination of gentle manual techniques aimed at restoring joint function, improving blood circulation, and reducing pain. This method can be used in the rehabilitation process after a hand fracture based on a doctor’s recommendation and under their supervision.
Mulligan Concept (Mobilization with Movement)
The Mulligan Concept is a manual therapy method that involves joint mobilization during movement. This approach can be applied in the rehabilitation after a hand fracture to improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and restore normal hand function. When using this method, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and perform manual techniques under the supervision of a qualified specialist.
Therapeutic Exercise
Therapeutic exercise, also known as physical therapy, is an essential part of rehabilitation after a hand fracture. It involves performing specific exercises aimed at restoring hand function, developing muscle strength and flexibility, improving blood circulation, and overall strengthening of the body. Here are links to videos demonstrating exercises for hand rehabilitation (insert links and anchors to relevant pages).
In conclusion, rehabilitation after a hand fracture is a complex and long process that requires patience, effort, and the correct approach. It is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, regularly perform exercises, undergo physiotherapy procedures, and maintain an adequate diet to achieve the maximum possible recovery of hand function.
By working with qualified specialists and following an individualized rehabilitation plan, most patients can return to normal life and restore their functionality after a hand fracture. However, it is important to remember that each case is unique, and recovery may take different periods of time and require different approaches. Patience, perseverance, and a positive mindset are key factors in successful rehabilitation.
Check the demo version of our sets of exercises for the Upper Limb Problems on YouTube.
You can find more information about the Upper Limbs Problems in our Library of Articles.
Our website presents sets of exercises for the upper limbs in the following areas: