A hip fracture is a serious injury that requires a long recovery. An important part of this process is rehabilitation, aimed at restoring patient’s functions and quality of life.
Conservative Treatment for Hip Fracture
In some cases of hip fracture, conservative treatment methods may be used. They can be used in combination to accelerate the healing and rehabilitation process.
Osteopathy in Rehabilitation After a Hip Fracture
Osteopathy is an alternative treatment method based on manual techniques and a holistic approach to the body. In the rehabilitation process after a hip fracture, osteopathy can be used as an auxiliary method to improve the quality of recovery.

Goals of Osteopathy in Rehabilitation
The main goals of osteopathy in rehabilitation after a hip fracture include:
- Restoring body balance and symmetry, which contributes to normalization of motor functions;
- Reducing pain and discomfort in the area of the injury;
- Improving circulation and lymph flow, which helps reduce swelling and inflammation;
- Stimulating the body’s self-regulation to accelerate recovery process.
Principles and Methods of Osteopathy
Osteopathy is based on the principle that the body has the ability to self-recovery. An osteopath uses manual methods, such as gentle impact on bones, muscles, joints, and fascia (connective tissues) to improve the functions of the musculoskeletal system and stimulate the body’s self-healing.
Conducting an Osteopathic Session
An osteopathic session begins with a collection of medical history and physical examination of any patient. An osteopath evaluates the patient’s condition, identifies functional disorders and imbalances, and then develops an individual treatment program. During the session, the osteopath carefully manipulates various body structures, moving them in certain directions to achieve the desired effect.
Integrating Osteopathy with Other Rehabilitation Methods
Osteopathy can be successfully integrated with other rehabilitation methods such as physiotherapy, massage, and therapeutic exercise to achieve the best recovery results after a hip fracture. It’s important for any patient to discuss the use of osteopathy with their treating physician and rehabilitation specialist to develop the most effective and safe comprehensive rehabilitation program.
Advantages and Limitations of Osteopathy
One of the advantages of osteopathy is its non-invasive and nature and targeting on natural self-regulation mechanisms of the body. Osteopathy can reduce the need for drug therapy and accelerate the recovery process. However, osteopathy is not a panacea and cannot replace other rehabilitation methods, especially in the case of serious injuries and complications.
The limitations of osteopathy include the need for a qualified and experienced specialist, as well as the individual nature of the approach, which may not be appropriate for all patients. In some cases, osteopathy may be contraindicated, so it’s important to consult with a doctor before starting treatment.
Pharmacopuncture in Rehabilitation After a Hip Fracture
Pharmacopuncture is an integrative treatment method that combines the principles of traditional Chinese medicine and modern pharmacology. In the rehabilitation process after a hip fracture, pharmacopuncture can be used as an auxiliary method for pain relief, reducing inflammation, and stimulating recovery processes.
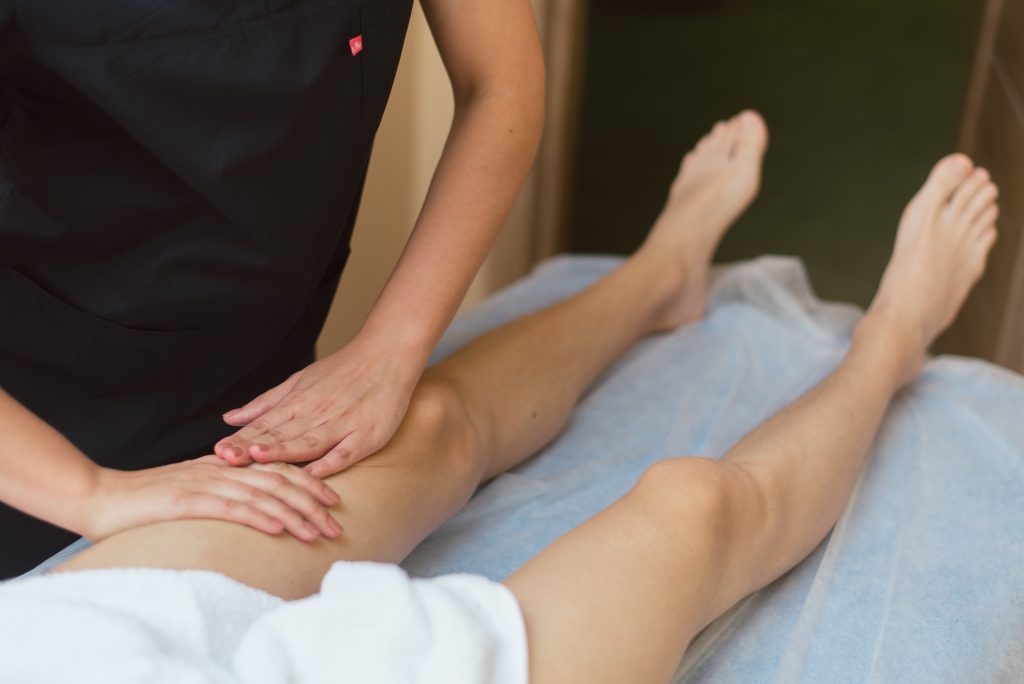
Basics of Pharmacopuncture
Pharmacopuncture involves the injection of drug substances into specific points on the body, corresponding to energy meridians, using thin needles. This allows the delivery of drug substances directly to the affected area, minimizing systemic side effects.
Use of Pharmacopuncture in Rehabilitation
Pharmacopuncture can be used to achieve the following goals in the rehabilitation process after a hip fracture:
- Reducing pain and discomfort in the area of the fracture;
- Reducing inflammation and swelling;
- Stimulating tissue regeneration and improving circulation;
- Improving musculoskeletal functions and joint mobility.
Types of Medications in Pharmacopuncture
Depending on the treatment goals, different types of medications, such as analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, vasodilators, chondroprotectors, etc. can be used in pharmacopuncture. It’s important that drugs are selected by a qualified specialist, considering the individual characteristics of the patient and the nature of his condition.
Advantages and Limitations of Pharmacopuncture
The advantages of pharmacopuncture include minimal side effects, high precision of action, quick effect, and the possibility of combining with other rehabilitation methods. However, pharmacopuncture is not a universal solution and may not be appropriate for all patients. In some cases, pharmacopuncture may be contraindicated due to allergies to drugs, blood clotting disorders, or other factors.
Integrating Pharmacopuncture with Other Rehabilitation Methods
Pharmacopuncture can be successfully combined with other rehabilitation methods such as physiotherapy, massage, therapeutic exercise, and psychological support. It’s important that the use of pharmacopuncture is coordinated with the treating physician and rehabilitation specialist to develop an individual comprehensive recovery program.
Specialist Qualification
One of the important aspects of successful use of pharmacopuncture is the qualification and experience of a specialist conducting the procedure. Pharmacopuncture requires special knowledge of anatomy, pharmacology, and principles of traditional Chinese medicine, so it’s crucial to select a specialist with appropriate education and experience.
Video: “Rehabilitation After a Hip Fracture”
Exercises for the pelvic girdle and hip joint. Set No.2 is aimed at strengthening the muscles
For additional information about the recovery process after a hip fracture, you can watch a video demonstrating exercises and rehabilitation recommendations.
Therapeutic Exercise in Rehabilitation After a Hip Fracture
Therapeutic exercise is one of the key rehabilitation methods after a hip fracture, aimed at restoring the functions of the musculoskeletal system, strengthening muscles and joints, and increasing the patient’s overall physical activity.

Goals and Principles of Therapeutic Exercise
The main goals of therapeutic exercise in rehabilitation after a hip fracture include:
- Restoring the strength and flexibility of muscles and ligaments;
- Improving joint mobility and stability;
- Reducing pain and inflammation;
- Enhancing movement coordination and overall endurance;
- Preventing complications and reducing the risk of repeated injuries.
Developing an Individual Therapeutic Exercise Program
The therapeutic exercise program is developed individually for each patient, considering their age, overall health condition, degree of injury, and recovery dynamics. It can include various exercises, such as active and passive movements, balance and stabilization exercises, as well as different types of load, gradually increasing as the patient recovers.
Methods and Techniques of Therapeutic Exercise
Various methods and techniques can be used in therapeutic exercises, such as:
- Isometric exercises for the activation and strengthening of muscles without joint movement;
- Isotonic exercises for the development of strength, flexibility, and endurance of muscles with joint movement;
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) for improving coordination, balance, and stability;
- Exercises in water or on equipment to reduce the load on the affected limb and facilitate the performance of movements.
The Role of the Therapeutic Exercise Specialist
The therapeutic exercise specialist plays a vital role in the patient’s recovery process after a hip fracture. They evaluate the patient’s condition, develop an individual exercise program, monitor the correct performance of exercises, and modify the program in accordance with the dynamics of recovery. It’s important to select an experienced and qualified specialist who can provide effective and safe rehabilitation.
Advantages and Limitations of Therapeutic Exercise
The advantages of therapeutic exercise lie in its safety and accessibility as a recovery method that can be adapted to the individual needs of each patient. Therapeutic exercise promotes the patient’s independence, improves their quality of life, and reduces the risk of repeated injuries.
The limitations of therapeutic exercise may include the need for long-term and regular performance of exercises, as well as possible limitations in movement or pain, which may hinder the execution of certain exercises. It’s important to consult with a doctor and a therapeutic exercise specialist before starting the program to ensure that the selected exercises are safe and suitable for a certain patient.
The Role of Diet in Rehabilitation After a Hip Fracture
Adequate nutrition plays a crucial role in the recovery process after a hip fracture. A balanced diet rich in nutrients promotes bone healing, muscle strengthening, and the overall improvement of the patient’s health condition.
Basic Principles of Diet During Rehabilitation
During rehabilitation after a hip fracture, the diet should meet the following requirements:
- Providing sufficient calories to maintain energy and repair tissues;
- High-protein food for the growth and repair of muscles, ligaments, and bones;
- Consumption of vitamins and minerals necessary for bone healing and immune system support;
- Hydrating the body with sufficient water intake.
Beneficial Foods for Bone Recovery
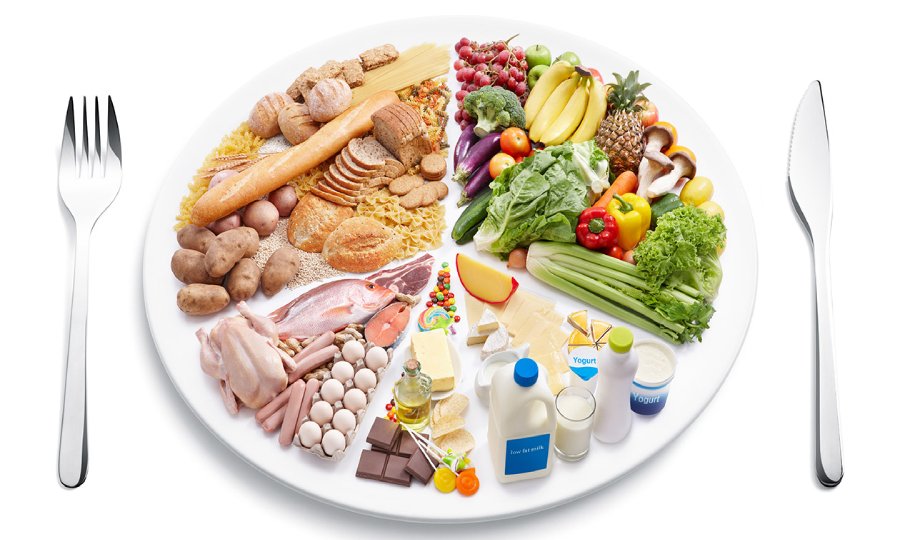

Patient’s diet should include foods rich in the following nutrients:
- Calcium: dairy products, dark green leafy vegetables, almonds, sesame seeds;
- Vitamin D: fatty fish, mushrooms, egg yolks, hard cheese;
- Magnesium: nuts, seeds, legumes, avocado, dark chocolate;
- Vitamin K: green leafy vegetables, broccoli, sorrel, cabbage;
- Proteins: meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, tofu.
Limiting Consumption of Certain Foods
During rehabilitation, patients should avoid foods that could affect bone healing or overall health condition:
- Sugar and high-sugar products;
- High-salt foods, such as sausages, smoked foods, canned foods;
- Alcohol and caffeine, as they may decrease calcium and magnesium absorption;
- Trans fats, which can be found in fast food, fried products, and some margarines, as they can contribute to inflammation and reduced nutrition.
Individual Approach to Diet
When creating a diet, it’s important to consider individual patient characteristics, such as age, gender, level of physical activity, concurrent diseases, and the body’s needs. In some cases, a consultation with a dietitian may be needed to develop an optimal nutrition plan.
Role of Dietary Supplements
During rehabilitation after a hip fracture, the use of dietary supplements containing vitamins and minerals necessary for bone healing and muscle strengthening may be beneficial. However, before starting any supplements, it’s important to consult with a doctor to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
Meal Schedule and Regimen
Adhering to a regular eating schedule and dividing food intake to 5-6 small meals throughout the day can contribute to better nutrient absorption and maintaining energy levels. It’s also important to pay attention to the quality of food and the preparation of healthy meals.
Physiotherapy in Rehabilitation After a Hip Fracture
Physiotherapy is one of the important components of rehabilitation after a hip fracture. Its goal is to restore the functions of the musculoskeletal system, improve circulation, and reduce pain and inflammation.
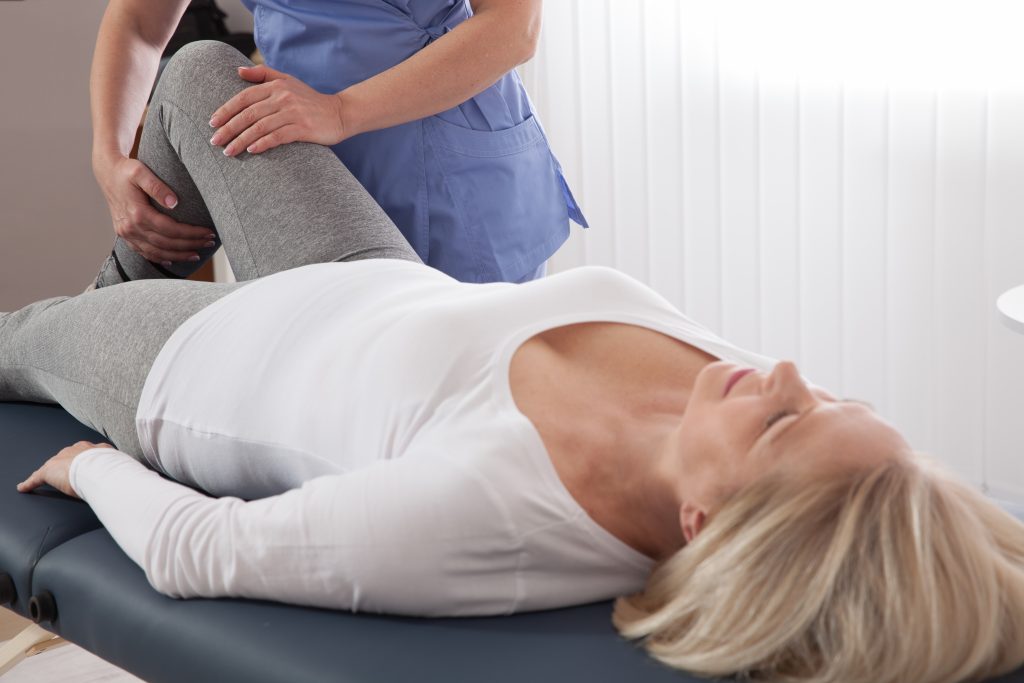

Main Methods of Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures involve many different methods that can be used during rehabilitation:
- Electrotherapy: the use of electric current to stimulate muscles, reduce pain, and accelerate tissue healing;
- Ultrasound therapy: the use of ultrasound waves to reduce inflammation and improve microcirculation of blood in the affected area;
- Magneto therapy: the use of magnetic fields to accelerate regeneration processes, reduce pain and inflammation;
- Laser therapy: the use of laser radiation to stimulate metabolic processes and activate cellular exchange;
- Mud therapy: the application of medicinal mud to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and accelerate tissue healing.
Selection of Physiotherapy Methods
Physiotherapy methods are selected by individual patient characteristics, the stage of fracture healing, comorbidities, and contraindications. It is necessary to consult with a physiotherapist to develop an individual treatment program.
Advantages and Limitations of Physiotherapy
The advantages of physiotherapy include:
- Safety and few side effects;
- Improved circulation, reduced pain, and inflammation;
- Stimulation of regeneration and strengthening of the musculoskeletal system;
- Can be used in combination with other rehabilitation methods.
Physiotherapy limitations may include:
- The need for regular procedures to achieve optimal results;
- Possible contraindications for some physiotherapy methods, especially in the presence of comorbidities or complications;
- Limited access to physiotherapy equipment or specialists in some regions.
Integration of Physiotherapy with Other Rehabilitation Methods
Physiotherapy can be successfully combined with other rehabilitation methods, such as therapeutic physical culture (TPC), massage, osteopathy, and alternative treatment methods. The combination of different approaches allows the creation of an integrated recovery program aimed at maximum improvement of musculoskeletal functions and the patient’s overall health.
Duration and Frequency of Physiotherapy Procedures
The duration and frequency of physiotherapy procedures are determined individually and depend on the patient’s condition, chosen treatment methods, and recovery dynamics. It is important to strictly follow the physiotherapist’s recommendations and regularly attend procedures to achieve the best results.
Monitoring Physiotherapy Outcomes
To evaluate the effectiveness of physiotherapy procedures, a physiotherapist may use various monitoring methods such as clinical examination, assessment of joint range of motion, muscle volume measurements, and functional tests. Monitoring results allow modifying the rehabilitation program and selecting the most effective treatment methods.
Therapeutic Massage in Hip Fracture Rehabilitation
Therapeutic massage is one of the key methods of rehabilitation after a hip fracture, contributing to the restoration of the functionality of the musculoskeletal system, improving microcirculation, and strengthening muscles.
Goals and Tasks of Therapeutic Massage
Therapeutic massage in rehabilitation after a hip fracture is aimed at:
- Reducing pain and inflammation;
- Improving blood circulation and lymph flow in the affected area;
- Relaxing tense muscles and strengthening the muscular corset;
- Restoring range of motion in joints and increasing flexibility;
- Prevention of scar formation and adhesion processes.
Main Techniques of Therapeutic Massage
Therapeutic massage can include various techniques and methods, such as:
- Classic massage: includes kneading, friction, patting, and vibration techniques;
- Segmental massage: focuses on specific zones or segments of the body associated with the affected area;
- Lymphatic drainage massage: aimed at stimulating lymph flow and reducing edema;
- Point massage: impacts certain points or zones on the body to stimulate regeneration and reduce pain.
Therapeutic Massage Process
Therapeutic massage should only be performed by an experienced massage specialist masseur or physiotherapist, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the stage of fracture healing. It is important to consult with a doctor before starting a massage course and strictly follow his recommendations.
Frequency and Duration of Massage Session
The frequency and duration of massage sessions are determined individually and depend on the patient’s condition, the stage of rehabilitation, and the chosen selected technique. Usually, it is recommended to perform massage every 2-3 days with a total course duration of 10 to 20 sessions. If necessary, the massage course can be extended or repeated after a certain period of time.
Advantages and Limitations of Therapeutic Massage
Advantages of therapeutic massage include:
- Reducing pain, inflammation, and swelling;
- Improving blood circulation and tissue nutrition;
- Restoring muscle function and joint flexibility;
- Prevention of scars and adhesions;
- Can be used in combination with other rehabilitation methods.
Limitations of therapeutic massage may include:
- The need for regular sessions to achieve the best results;
- Possible contraindications for massage in certain conditions or comorbidities;
- The need for access to a qualified massage specialist or physiotherapist.
Integrating Therapeutic Massage with Other Rehabilitation Methods
Therapeutic massage can be successfully combined with other rehabilitation methods, such as physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapy, osteopathy, and alternative treatment methods. Combining different approaches gives opportunity for an integrated recovery program aimed at maximum improvement of the musculoskeletal functions and the overall health condition of the patient.
Monitoring Therapeutic Massage Results
The effectiveness of therapeutic massage can be evaluated using various methods such as clinical examination, muscle volume measurements, evaluation of the range of joint motion, and functional tests. Monitoring results allow modifying the rehabilitation program and determining additional treatment methods if necessary.
Modern Rehabilitation Techniques
There are many modern rehabilitation techniques that can be used in combination for effective recovery after a hip fracture.
Kinesio Taping
Kinesio Taping is a method of applying special elastic tapes to the skin that provide support for muscles and joints, reduce swelling, and improve blood circulation.
Manual Therapy
Manual therapy is a complex of manual techniques aimed at restoring joint mobility, reducing pain, and normalizing the functions of the musculoskeletal system.
Pilates
Pilates is a system of exercises aimed at developing muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination. These exercises can be adapted for patients with hip fractures to improve their health condition.
Yoga Therapy
Yoga therapy is an integrative approach to treatment based on the principles of yoga. It can help patients with a hip fracture reduce stress, improve flexibility and muscle strength, and learn to manage pain.
Mechanotherapy
Mechanotherapy is a treatment method that uses mechanical impact on tissues and joints. It may involve the use of special equipment or performing exercises with a specific load.
It is important to remember that each body is unique, and rehabilitation techniques should be selected taking into account individual characteristics of a patient and under the supervision of a doctor. Self-use of methods can lead to a aggravation of health condition and the occurrence of complications.
Why Rehabilitation is So Important
Rehabilitation after a hip fracture plays a key role in restoring the functions of the musculoskeletal system and the patient’s quality of life. It helps improve joint mobility, strengthen muscles, and return the patient to normal life.
Sequelae of a Fracture
A hip fracture can have serious sequelae consequences for a patient’s health, such as limited mobility, chronic pain, and even disability. A properly selected rehabilitation program helps to reduce the risk of these complications and ensures quick and effective recovery.
Possible Complications
Possible complications after a hip fracture include infectious complications (thrombophlebitis, osteomyelitis), secondary deformities, impaired circulation and innervation, and chronic pain. Rehabilitation helps prevent or reduce the risk of these complications, improving the patient’s overall condition.
Individual Approach to Rehabilitation
The rehabilitation program should be developed taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient, type of fracture, age, general health condition, and other factors. The orthopedic surgeon and rehabilitation specialist determine the most appropriate methods and techniques for each case.
Adapting the Rehabilitation Program
Depending on the stage of recovery and changes in the patient’s condition, the rehabilitation program can be corrected. This allows to achieve the maximum effect of the procedures performed and to reduce the recovery time.
Patient Motivation and Support
Patient motivation and support play an important role in the rehabilitation process. Patient engagement in the treatment process and informing about his progress can significantly increase the effectiveness of rehabilitation and improve outcomes.
Returning to Everyday Life
The main goal of rehabilitation after a hip fracture is to return the patient to normal life, restoring the ability to move and perform everyday actions.

Social Adaptation
During the rehabilitation process, it’s important to pay attention to the patient’s social adaptation. Psychological support and assistance in solving everyday issues can help the patient cope more easily with changes caused by the injury.
Returning to Work and Hobbies
Recovery after a hip fracture can take a long period of time, but many patients return to their regular activities, work, and hobbies. Rehabilitation programs can be adapted to ensure the maximum possible return to the previous level of activity.
Conclusion
Rehabilitation after a hip fracture is an integral part of the recovery process. Timely onset and properly selected rehabilitation program can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life and return him or her to an active life.
For a deeper understanding and additional information about various exercises for rehabilitation after a hip fracture, we recommend watching video exercises on our website (or add a link to the exercises). This will help you perceive possible treatment methods and their practical application, and also allow you to select the most suitable set of exercises for your case.
Remember, an important condition for successful recovery is an individual approach and strict adherence to the recommendations of your doctor. We wish you good luck on your way to health and speedy recovery!
Check out the demo version of our sets of exercises for the Lower Limb Problems on YouTube
You can find more information about the Lower Limb Problems in our Library of Articles
Our website presents the following sets of exercises for rehabilitation of the pelvic girdle and hip joint, knee joint and ankle joint:
EXERCISES FOR THE PELVIC GIRDLE AND HIP JOINT. SET №1 IS AIMED AT MUSCLE STRETCHING (IMPROVEMENT OF FLEXIBILITY OF THE MUSCULAR APPARATUS) AND INCREASE OF THE RANGE OF JOINT MOVEMENT
EXERCISES FOR THE PELVIC GIRDLE AND HIP JOINT. SET №2 IS AIMED AT STRENGTHENING THE MUSCLES
EXERCISES FOR THE KNEE JOINT. SET №3 IS AIMED AT STRETCHING THE MUSCLES (IMPROVING THE FLEXIBILITY OF THE MUSCULAR APPARATUS) AND INCREASING THE RANGE OF JOINT MOVEMENT
EXERCISES FOR THE KNEE JOINT. SET 4A IS AIMED AT STRENGTHENING THE MUSCLES. INITIAL STAGE
EXERCISES FOR THE KNEE JOINT. SET 4B IS AIMED AT STRENGTHENING THE MUSCLES. MID STAGE
EXERCISES FOR THE KNEE JOINT. SET 4C IS AIMED AT STRENGTHENING THE MUSCLES. ADVANCED STAGE
EXERCISES FOR THE ANKLE JOINT. SET №5 IS AIMED AT STRETCHING THE MUSCLES (IMPROVEMENT OF FLEXIBILITY OF THE MUSCULAR APPARATUS) AND INCREASE OF THE RANGE OF JOINT MOVEMENT
EXERCISES FOR THE ANKLE JOINT. SET №6D IS AIMED AT STRENGTHENING OF THE MUSCLES AND IMPROVEMENT OF PROPRIOCEPTION AND STABILITY OF THE ANKLE AND ENTIRE LOWER LIMB. INITIAL STAGE
EXERCISES FOR THE ANKLE JOINT. SET №6E IS AIMED AT STRENGTHENING OF THE MUSCLES AND IMPROVEMENT OF PROPRIOCEPTION AND STABILITY OF THE ANKLE AND ENTIRE LOWER LIMB. MID STAGE
EXERCISES FOR THE ANKLE JOINT. SET №6F IS AIMED AT STRENGTHENING OF THE MUSCLES AND IMPROVEMENT OF PROPRIOCEPTION AND STABILITY OF THE ANKLE AND ENTIRE LOWER LIMB. ADVANCED STAGE
In addition to the listed sets of exercises please check out article and sets of exercises for the Post-traumatic Rehabilitation of Gait Disorders



