The process of recovery after a tibia fracture can be lengthy and requires the right approach. Explore our exercise complex and treatment methods developed based on Israeli protocols, available on the Video Exercises for Tibia Fracture Rehabilitation website, to start your way to recovery today.
When Can You Begin Home Rehabilitation?
Experiencing a leg fracture is a significant challenge, and the way to full recovery requires time, patience, and the right approach. Our subscription provides you access to expertly designed video exercises that will help you safely and effectively recover at home.
After a leg fracture, it is crucial to start rehabilitation at the optimal time:
- Completion of the Acute Phase: Before beginning home exercises, the acute phase of inflammation and pain should subside. This usually takes several weeks after the injury.
- Consultation with a Doctor: Prior to starting home exercises, it is necessary to obtain permission from your treating physician or physical therapist. They can assess your current condition and provide recommendations regarding the type and intensity of exercises.
What You Get with the Subscription
- Video Instructions: Get access to our detailed videos demonstrating the correct execution of exercises, reducing the risk of injuries and expediting the recovery process.
- Written Instructions and Infographics: In addition to videos, you will receive written instructions and informative infographics to understand better each exercise and its goals.
- Optimized Repetition Count: Our exercises come with recommendations on the number of repetitions and sets, ensuring a gradual and safe increase in workload.
Benefits of Home Rehabilitation
- Convenience and Flexibility: You can perform exercises at your convenience and pace.
- Personalized Approach: Our program accommodates different stages of recovery and is adapted to meet individual needs
- Continuous Access: You can revisit the videos and instructions as many times as needed.
Subscribing to our program is your step towards independent and active recovery!
Watch Rehabilitation Exercises After Leg Fracture Video
Video: “Exercises for the Lower Limb Problems“
EXERCISES FOR THE ANKLE JOINT. SET №6E IS AIMED AT STRENGTHENING OF THE MUSCLES AND IMPROVEMENT OF PROPRIOCEPTION AND STABILITY OF THE ANKLE AND ENTIRE LOWER LIMB. MID STAGE
For additional information about the recovery process you can watch a video demonstrating exercises and rehabilitation recommendations.
Key Principles of Tibia Fracture Rehabilitation
A tibia fracture is a serious injury that requires a comprehensive rehabilitation approach. Rehabilitation after such a fracture aims not only to restore bone tissue but also to improve the functionality of the entire leg. Here are the key principles to consider.
Why Early Mobilization Matters
Early mobilization plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process. It helps prevent complications such as blood stagnation, thrombosis, and muscle atrophy. Initiating light exercises and active movements within the pain threshold early on contributes to faster healing and improved blood circulation.
Goals of the Rehabilitation Process
The goals of rehabilitation include restoring a full range of motion in the joints, strengthening muscles, ensuring stability and balance, and returning to daily activities and sports. It is also essential to pay attention not only to the physical aspects of recovery but also to the patient’s psychological well-being, as a long rehabilitation process can be emotionally challenging.
Personalized Approach to Rehabilitation
Every case of tibia fracture is unique and therefore requires an individualized approach to treatment and rehabilitation. Factors such as the patient’s age, general health condition, pre-injury level of physical activity, and specific injury characteristics should be taken into account. The rehabilitation plan should be adapted to the patient’s individual needs, which may include various forms of therapy, exercises, and, if necessary, the use of orthopedic devices.
Effective rehabilitation requires close collaboration between the patient, doctors, physiotherapists, and other specialists. It is crucial to follow strictly the recommendations of healthcare professionals and attend all scheduled rehabilitation sessions to achieve the maximum benefit from treatment.
Stages of Rehabilitation after Tibia Fracture
Rehabilitation after a tibia fracture is a multi-stage process that requires patience and consistency. Understanding each stage will help patients better navigate the recovery process. Here are the main stages.

Acute Stage of Recovery
The acute stage begins immediately after the injury and lasts for the first few weeks. During this period, the primary goals are pain management, reducing swelling, and preventing complications. Rest is crucial at this stage, and the proper use of immobilizing bandages or casts is essential to ensure proper bone healing. Gentle exercises, such as passive movements of the toes and knee flexion-extension, may be recommended to maintain blood circulation.
Subacute Stage of Recovery
The subacute stage typically begins around 3-6 weeks after the injury and continues until the bone has fully healed, which can take several months. During this period, the focus shifts to gradual restoration of mobility and muscle strengthening. Physical therapists may introduce exercises to improve range of motion, strengthen calf muscles, and enhance overall mobility. The key is a the balance between muscle activation and avoiding excessive stress on the healing bone.
Late Stage of Recovery
At the late stage of recovery, which occurs after the bone has completely healed, the emphasis is on returning to normal life and activities. Exercises become more intensive, including balance, coordination, and lower limb strengthening exercises. During this period, it is important to continue physical exercises to prevent muscle atrophy and maintain overall physical fitness. Gradually increased load is also introduced, allowing to return to a more active lifestyle, including sports and work.
At each stage, regular medical monitoring and close collaboration with the rehabilitation team are essential. Patients should carefully follow the instructions and recommendations of specialists to maximize recovery and minimize the risk of complications.
Treatment and Recovery Methods
After a tibia fracture, it is important to apply a comprehensive approach to treatment and recovery, which includes various methods. These methods are aimed at accelerating the healing process, reducing pain, restoring function, and preventing long-term complications.
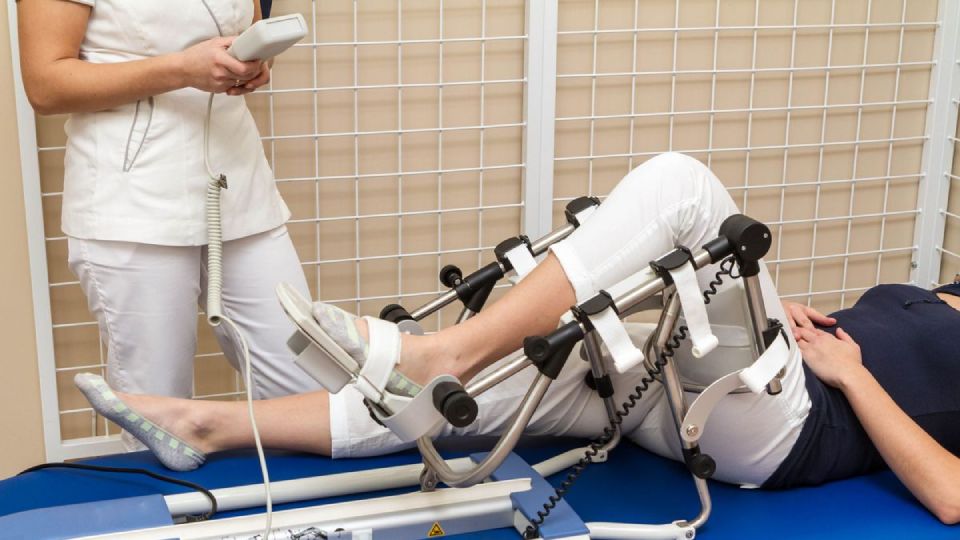
Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy is one of the key elements of recovery after a tibia fracture. It involves exercises aimed at strengthening muscles, improving joint mobility, and increasing overall endurance. Starting with passive exercises, which are performed without any load on the injured area, and gradually progressing to active exercises, physical therapy helps restore normal leg function. Additionally, special exercises for balance and coordination may be included.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on restoring a patient’s ability to perform everyday tasks and activities. Therapists help patients adapt to the limitations related to the fracture and develop individual strategies for performing household and work-related duties.
Massage and Rubbing
Massage and rubbing can be used to reduce muscle tension, improve blood circulation, and alleviate pain in the injured area. These methods also promote relaxation and can enhance general well-being of the patient.
Use of Orthopedic Devices and Aids
Various orthopedic devices, such as braces, orthoses, or special footwear, may be used to support the healing tibia and prevent additional injuries. These devices help stabilize the tibia, distribute the load, and provide the necessary support while moving.
These treatment and recovery methods complement each other and provide comprehensive support throughout the rehabilitation process after a tibia fracture. It is important to follow strictly the recommendations of doctors and therapists and regularly attend all planned treatment and rehabilitation sessions to achieve the best results.
Exercises for Strengthening and Rehabilitating the Tibia
After a tibia fracture, exercises play a crucial role in accelerating the recovery process, strengthening muscles, and restoring normal limb function. The exercise program should be gradual and tailored to the individual needs of the patient.
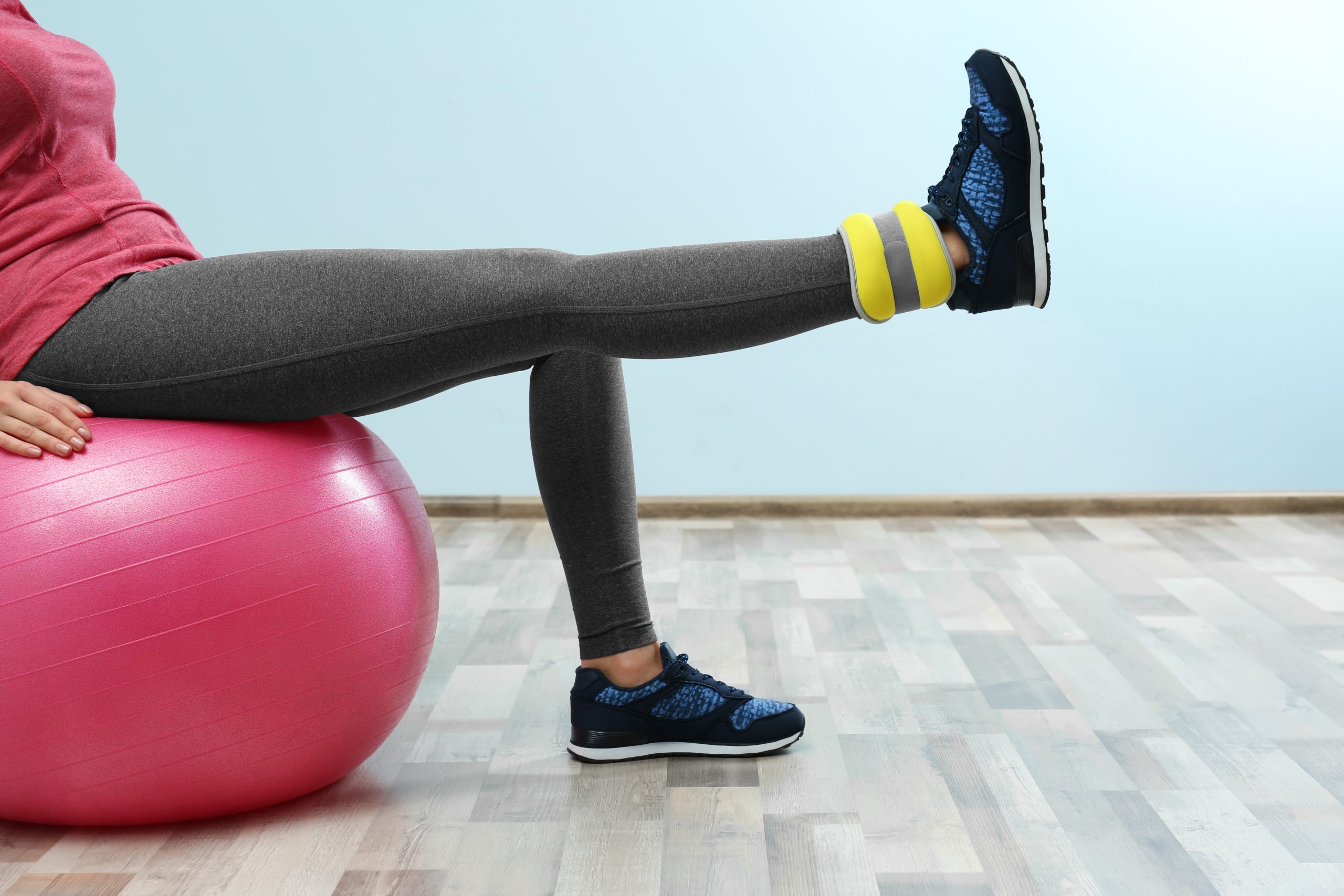

Exercises at the Initial Stage
During the initial stage of recovery, when the tibia has not fully healed yet, it is recommended to use low-impact exercises. These may include:
- Passive movements: movements performed with the assistance of a physical therapist or with the help of the other hand, without active involvement of the calf muscles
- Isometric exercises: muscle tension without joint movement, such as attempts to contract the calf muscles when the leg is in a cast.
- Toe exercises: bending and straightening the toes to stimulate blood circulation in the leg.
Exercises at the Subacute Stage
As your condition improves and pain decreases, you can incorporate more active exercises:
- Stretching: Gentle stretching of tightened muscles to prevent muscle contraction and improve mobility.
- Strength exercises: Using light weights or resistance bands to strengthen gradually the calf muscles.
- Balance exercises: Standing on one leg, initially with support, and then without support.
Exercises at the Late Stage
During the late stage of recovery, when the bone has fully healed, the focus shifts to returning to full functionality:
- Cardiovascular exercises: Walking, swimming, or stationary cycling to improve overall fitness and endurance.
- Strength exercises: Using heavier weights or resistance machines to strengthen the muscles of the entire leg.
- Functional exercises: Simulating everyday movements, such as stair climbing, to improve coordination and restore normal mobility.
It is important to start each workout with a warm-up and finish with stretching. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercises as your condition improves. Remember that all exercises should be performed without pain, and if discomfort arises, you should stop the workout immediately and consult with your doctor.
Physiotherapeutic Procedures
Physiotherapeutic procedures are an integral part of recovery after a tibia fracture. They help expedite the healing process, reduce pain, and restore limb function. Here are a few key procedures commonly used in such cases:
Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy involves using electrical impulses to stimulate muscles and nerves. This helps reduce pain, improve blood circulation, and helps in the recovery of damaged tissues. Examples include TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) and electromyostimulation.
Ultrasound Therapy
Ultrasound therapy uses high-frequency sound waves to improve local blood circulation and accelerate tissue healing processes. This therapy can contribute to reducing swelling and enhancing mobility in the affected area.
Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy involves performing exercises in water, which reduces the load on the injured leg. Water provides natural resistance and support, allowing exercises to be performed with less pain and risk of injury.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy uses low-level lasers to reduce inflammation and pain at the site of injury. It promotes tissue recovery and regeneration at the cellular level.
Manual Therapy
Manual therapy includes various hands-on techniques such as massage and joint mobilization, aimed at improving flexibility, reducing pain, and restoring function.
Heat Therapies
The application of heat, such as hot packs, hot baths, or infrared lamps, helps relax muscles, improve blood circulation, and alleviate pain.
Each of these procedures has its indications and contraindications, and they should be carried out under the supervision of a qualified physiotherapist. It is important to remember that physiotherapeutic procedures are most effective when they are part of a comprehensive rehabilitation plan that includes exercises, proper nutrition, and, if necessary, psychological support.
Diet and Lifestyle During Rehabilitation
Diet and lifestyle play a crucial role in the rehabilitation process after a tibia fracture. A healthy lifestyle and balanced diet contribute to faster recovery, bone strengthening, and general well-being.

The Role of Balanced Diet
Adequate diet provides the body with all necessary nutrients for bone tissue recovery and muscle maintenance. The diet should be rich in:
- Proteins: Essential for tissue repair and growth. Sources of protein include meat, fish, eggs, legumes, and dairy products.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Extremely important for bone health. Calcium is found in dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and tofu, while vitamin D can be obtained from fish, egg yolks, and sunlight exposure.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that enhance immune function and support overall recovery.
- Healthy Fats: Such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and nuts, contribute to reducing inflammation and improving general
Hydration
Adequate hydration is essential for tissue healing and general well-being. Drinking enough water helps transport nutrients to the injured area and eliminate waste products.
Avoidance of Social Habits
During the rehabilitation period, it is crucial to avoid habits that can hinder the healing process, such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These habits can impair blood circulation and delay recovery.
Stress Management
Managing stress and maintaining a positive outlook can positively impact the healing process. Chronic stress can hinder recovery, so incorporating relaxation techniques and seeking emotional support is beneficial.
Adequate Rest
Proper rest and sleep are essential for tissue repair and overall recovery. Ensure you get enough rest to allow your body to heal effectively.
Remember that individual nutritional needs may vary, so consulting with a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized guidance during your rehabilitation is advisable.
Importance of Adequate Rest and Sleep
Quality rest and adequate sleep are critically important for the recovery process. Sleep contributes to tissue regeneration, strengthens the immune system, and reduces stress. Adults are recommended to get 7-9 hours of sleep every night.
Avoidance of Social Habits
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can slow down the bone healing process and worsen general health. It is important to reduce or eliminate these habits for more effective recovery.
Moderate Physical Activity
Physical activity is important for maintaining blood circulation, preventing muscle atrophy, and improving mood. However, it is important to avoid excessive stress on the injured shin and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and balanced diet helps accelerate the recovery process, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall quality of life during rehabilitation after a tibia fracture.
Psychological Support During the Recovery Process
Providing strategies and methods to reduce stress and anxiety that can accompany the recovery process.
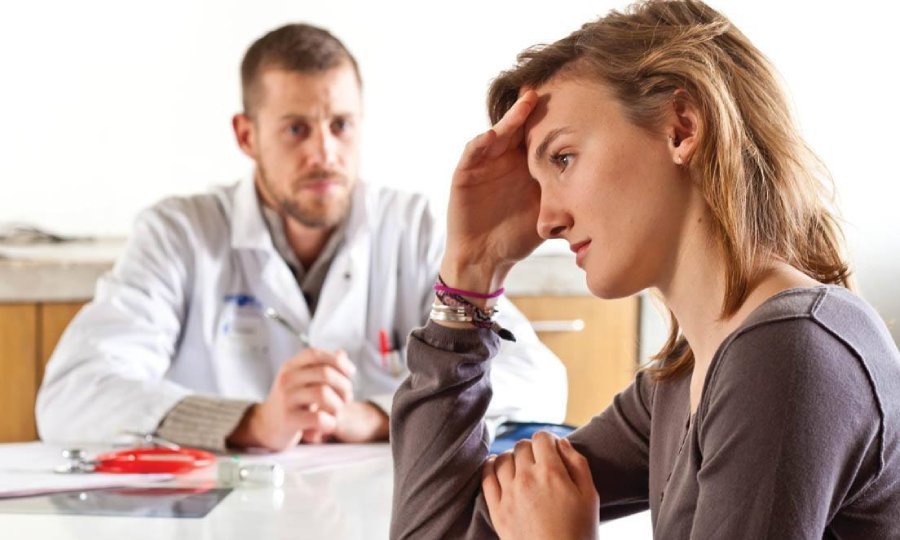

Why Psychological Support is Important
Psychological support is a key element in the recovery process, helping patients adapt to changes and maintain a positive outlook.
Prevention of Complications and Recurrences
After a tibia fracture, it is important to take certain measures to avoid complications and prevent recurring injuries. Here are several key strategies for preventing complications and recurrences.
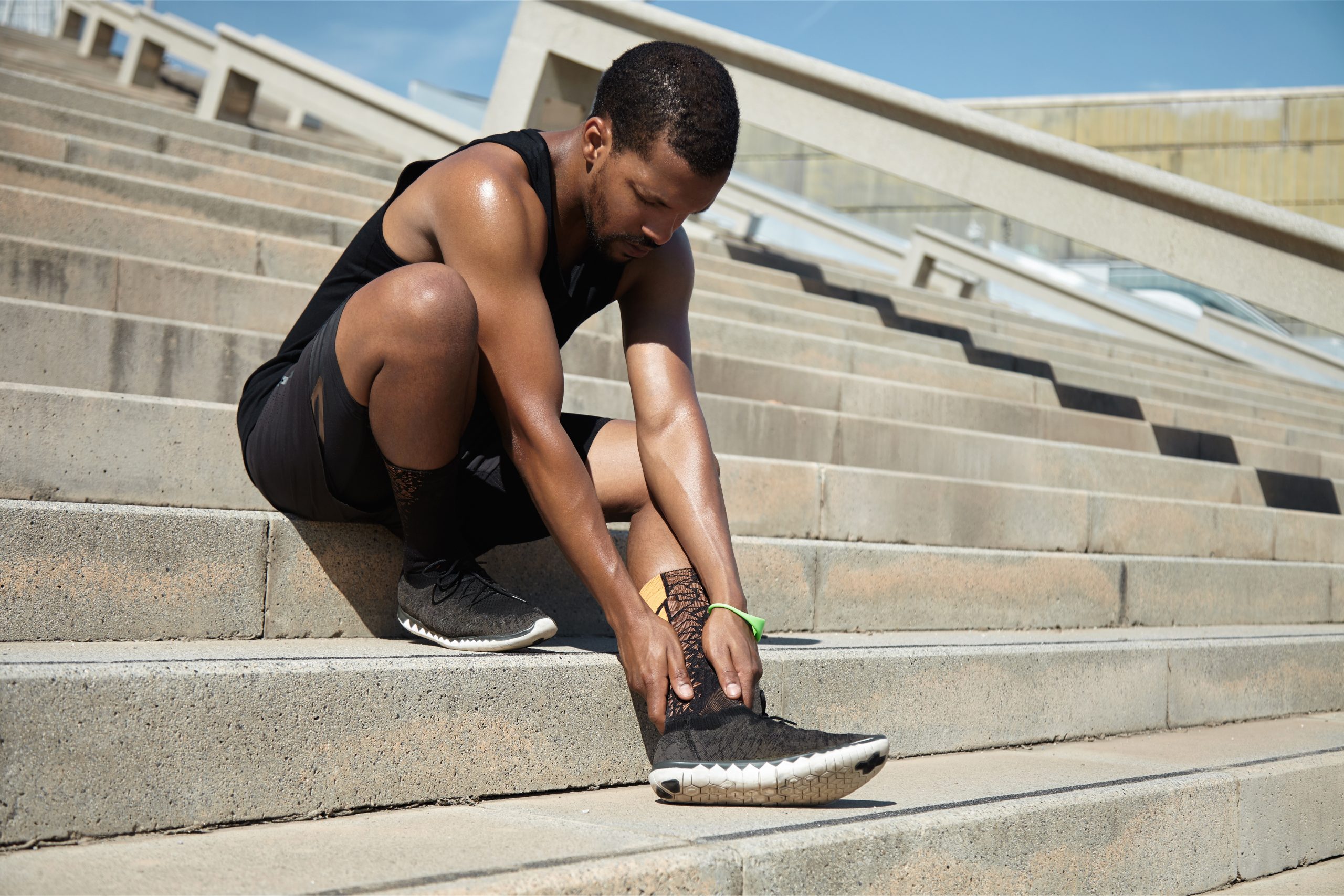

Precautions in Everyday Life
- Avoid Excessive Strain: After a tibia injury, it is important to avoid activities that could be an excessive pressure on the healing bone. Be cautious when lifting heavy objects and avoid intense exercises until you have fully recovered.
- Maintain Proper Posture and Balance: Incorrect posture can increase the risk of falls and recurring injuries. Work on improving your balance and coordination to reduce the possibility of falls.
- Use Supportive Devices: During the recovery period, you may need special orthopedic devices such as crutches, walkers, or braces to provide additional support and stability.
Regular Medical Check-ups
- Regularly visit your doctor to monitor the healing and recovery process. The doctor can track your progress and promptly identify any signs of potential complications.
- Follow all the doctor’s recommendations regarding drugs and care for the injured area.
Strategies for Preventing Recurrent Injuries
- Muscle Strengthening: Regular exercises to strengthen the muscles of the tibia and the entire lower extremity can help reduce the risk of future injuries.
- Stretching and Flexibility: Stretching exercises promote flexibility, which can help prevent injuries related to sudden movements.
- Gradual Increase in Load: When returning to physical activity, it is important to increase gradually the load to avoid overloading the healing bone and muscles.
Remember that preventing complications and recurrences is an ongoing process that requires attention and patience. Following these recommendations will help accelerate the recovery process and reduce the risk of future health problems.

Frequently asked Questions
Question 1: How long will the rehabilitation after a shin fracture last?
Answer: The duration of rehabilitation after a shin fracture depends on various factors, including the type of fracture, overall general health condition, and individual response to treatment. Typically, it takes between 2 to 6 months.
Question 2: Is it necessary to wear an orthopedic device after a shin fracture?
Answer: In most cases, it is recommended to wear an orthopedic device such as a cast or brace after a shin fracture to maintain the proper position and protect it during the healing process.
Question 3: Is it possible to return to sports after a shin fracture?
Answer: Yes, returning to sports after a shin fracture is possible, but it should be done gradually and under the guidance of a physician and a rehabilitation specialist.
Question 4: What precautions should be taken after the cast is removed?
Answer: After the cast is removed, it is important to avoid excessive strain on the shin, use supportive bandages or orthotics if necessary, and gradually increase physical activity.
Question 5: How to prevent muscle atrophy during prolonged immobilization?
Answer: To prevent muscle atrophy during prolonged immobilization, it is important to engage in gentle exercises for the muscles not affected by immobilization and follow the doctor’s recommendations for muscle activation after immobilization is over.
Question 6: What type of footwear is recommended after a shin fracture?
Answer: After a shin fracture, it is recommended to wear comfortable, supportive footwear that does not compress the shin to minimize the load on the shin and ensure comfort.
Question 7: Can yoga help in the rehabilitation process?
Answer: Yoga can be beneficial in the rehabilitation process for improving flexibility, balance, and overall relaxation, but it should be practiced with caution and under the guidance of an experienced instructor.





